填充和描邊屬性
繪製
可以透過設定節點上的兩個屬性來完成基本著色:fill(填充)和 stroke(描邊)。使用 fill 可以設定物件內部的顏色,而 stroke 則設定圍繞物件繪製的線條的顏色。您可以使用與 HTML 中相同的 CSS 顏色命名方案,無論是顏色名稱(如 red)、rgb 值(如 rgb(255 0 0))、十六進位制值等。
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<svg width="160" height="140" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<rect
x="10"
y="10"
width="100"
height="100"
stroke="blue"
fill="purple"
fill-opacity="0.5"
stroke-opacity="0.8"
stroke-width="15" />
</svg>
此外,您還可以在 SVG 中單獨指定 fill 或 stroke 的不透明度。這些由 fill-opacity 和 stroke-opacity 屬性控制。
描邊
除了其顏色屬性外,還有一些其他屬性可用於控制線上條上繪製描邊的方式。

<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<svg width="160" height="140" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<line x1="40" x2="120" y1="20" y2="20" stroke="black" stroke-width="20" stroke-linecap="butt"/>
<line x1="40" x2="120" y1="60" y2="60" stroke="black" stroke-width="20" stroke-linecap="square"/>
<line x1="40" x2="120" y1="100" y2="100" stroke="black" stroke-width="20" stroke-linecap="round"/>
</svg>
stroke-width 屬性定義了描邊的寬度。描邊在路徑周圍居中繪製。在上例中,路徑顯示為粉色,描邊顯示為黑色。
影響描邊的第二個屬性是 stroke-linecap 屬性,如上所示。這控制了線條末端的形狀。
stroke-linecap 有三個可能的值
butt用一個平直的邊緣封閉線條,該邊緣垂直於描邊的方向(成 90 度)並延伸到其末端。square的外觀基本相同,但會將描邊稍微延伸到實際路徑之外。超出路徑的描邊距離是stroke-width的一半。round在描邊的末端產生圓角效果。此曲線的半徑也由stroke-width控制。
使用 stroke-linejoin 控制兩個線段之間的連線點的繪製方式。

<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<svg width="160" height="280" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<polyline points="40 60 80 20 120 60" stroke="black" stroke-width="20"
stroke-linecap="butt" fill="none" stroke-linejoin="miter"/>
<polyline points="40 140 80 100 120 140" stroke="black" stroke-width="20"
stroke-linecap="round" fill="none" stroke-linejoin="round"/>
<polyline points="40 220 80 180 120 220" stroke="black" stroke-width="20"
stroke-linecap="square" fill="none" stroke-linejoin="bevel"/>
</svg>
這些折線中的每一條都有兩個線段。這兩個線段連線處的連線點由 stroke-linejoin 屬性控制。此屬性有三個可能的值。miter 會將線條稍微延伸到其正常寬度之外,以建立只有一個角度的方形轉角。round 建立一個圓角線段。bevel 建立一個新角度,以幫助兩個線段之間的過渡。
最後,您還可以透過指定 stroke-dasharray 屬性來使用虛線型別的描邊。
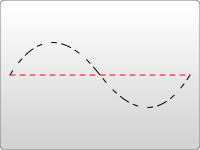
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<svg width="200" height="150" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<path d="M 10 75 Q 50 10 100 75 T 190 75" stroke="black"
stroke-linecap="round" stroke-dasharray="5,10,5" fill="none"/>
<path d="M 10 75 L 190 75" stroke="red"
stroke-linecap="round" stroke-width="1" stroke-dasharray="5,5" fill="none"/>
</svg>
stroke-dasharray 屬性可以接受一系列由逗號和/或空格分隔的數字作為其引數。
第一個數字指定了填充區域的距離,第二個數字指定了未填充區域的距離。因此,在上例中,第二個路徑填充 5 個畫素單位,有 5 個空白單位,然後是下一個 5 個單位的虛線。您可以指定更多數字以獲得更復雜的虛線模式。第一個示例指定了三個數字,在這種情況下,渲染器會迴圈使用這些數字兩次以建立均勻的圖案。因此,第一個路徑渲染 5 個填充,10 個空白,5 個填充,然後迴圈回到建立 5 個空白,10 個填充,5 個空白。然後模式重複。
還有其他 stroke 和 fill 屬性可用,包括 fill-rule,它指定如何填充重疊自身的形狀;stroke-miterlimit,它確定描邊是否應繪製斜接;以及 stroke-dashoffset,它指定在直線上虛線陣列的起始位置。
繪製順序
填充和描邊的繪製順序可以透過 paint-order 屬性進行控制。
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<svg width="400" height="180" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<polyline
points="40 80 80 40 120 80"
stroke-width="15"
stroke="black"
fill="coral"
paint-order="fill" />
<polyline
points="40 140 80 100 120 140"
stroke-width="15"
stroke="black"
fill="coral"
paint-order="stroke" />
</svg>
對於第一個形狀,填充在描邊之前渲染,因此黑色描邊出現在填充之上。對於第二個形狀,描邊在填充之前渲染。
使用 CSS
除了在物件上設定屬性外,您還可以使用 CSS 為填充和描邊設定樣式。並非所有屬性都可以透過 CSS 設定。通常可以使用與繪製和填充相關的屬性,因此 fill、stroke、stroke-dasharray 等都可以透過這種方式設定,以及下面顯示的漸變和圖案版本。諸如 width、height 或 <path> 命令之類的屬性不能透過 CSS 設定。最簡單的方法是進行測試,找出哪些可用,哪些不可用。
注意: SVG 規範嚴格區分了“屬性”和其他屬性。前者可以透過 CSS 修改,後者則不能。
CSS 可以透過 style 屬性內聯插入到元素中
<rect x="10" height="180" y="10" width="180" style="stroke: black; fill: red;"/>
或者可以將其移至您包含的特殊樣式部分。但是,與 HTML 中將此類部分放在 <head> 部分不同,它包含在一個稱為 <defs> 的區域中。
<defs> 代表定義(definitions),在這裡您可以建立不直接出現在 SVG 中但被其他元素使用的元素。
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<svg width="200" height="200" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<defs>
<style><![CDATA[
#MyRect {
stroke: black;
fill: red;
paint-order: stroke;
}
]]></style>
</defs>
<rect x="10" height="180" y="10" width="180" id="MyRect"/>
</svg>
將樣式移到這樣的區域可以更輕鬆地調整大量元素的屬性。您還可以使用諸如 **:hover 偽類**之類的東西來建立懸停效果
#MyRect:hover {
stroke: black;
fill: blue;
}
您還可以透過 正常的 XML 樣式表語法為您的 CSS 規則指定外部樣式表
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="no"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/css" href="style.css"?>
<svg width="200" height="150" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" version="1.1">
<rect height="10" width="10" id="MyRect"/>
</svg>
其中 style.css 的內容大致如下
#MyRect {
fill: red;
stroke: black;
}