使用 CSS Painting API
CSS Paint API 旨在讓開發者以程式設計方式定義影像,然後這些影像可以在任何可以呼叫 CSS 影像的地方使用,例如 CSS 的 background-image、border-image、mask-image 等。
要以程式設計方式建立 CSS 樣式表使用的影像,我們需要經歷幾個步驟:
- 使用
registerPaint()函式定義一個 paint worklet。 - 註冊 worklet。
- 包含
paint()CSS 函式。
為了詳細說明這些步驟,我們將從建立一個半高亮背景開始,就像這個標題一樣。

注意: 有關完整的演示以及 原始碼,請參閱 CSS Painting API 示例。
CSS Paint Worklet
在外部指令碼檔案中,我們使用 registerPaint() 函式來命名我們的 CSS Paint Worklet。它接受兩個引數。第一個是我們給 worklet 起的名字——這個名字將在我們的 CSS 中用作 paint() 函式的引數,當我們想將此樣式應用於某個元素時。第二個引數是實現所有魔力的類,它定義了上下文選項以及在將渲染到將成為我們影像的二維畫布上。
registerPaint(
"header-highlight",
class {
/*
* define if alpha transparency is allowed alpha
* is set to true by default. If set to false, all
* colors used on the canvas will be fully opaque
*/
static get contextOptions() {
return { alpha: true };
}
/*
* ctx is the 2D drawing context
* a subset of the HTML Canvas API.
*/
paint(ctx) {
ctx.fillStyle = "hsl(55 90% 60% / 100%)";
ctx.fillRect(0, 15, 200, 20); /* order: x, y, w, h */
}
},
);
在此類示例中,我們使用 contextOptions() 函式定義了一個上下文選項:我們返回了一個物件,說明允許 alpha 透明度。
然後,我們使用 paint() 函式在畫布上進行繪製。
paint() 函式可以接受三個引數。在這裡,我們提供了一個引數:渲染上下文(我們稍後會更詳細地介紹),通常用變數名 ctx 來引用。2D Rendering Context 是 HTML Canvas API 的一個子集;Houdini 可用的版本(稱為 PaintRenderingContext2D)是 Canvas API 的一個更小的子集,它包含了 Canvas API 的大部分功能,但 例外 是 CanvasImageData、CanvasUserInterface、CanvasText 和 CanvasTextDrawingStyles API。
我們將 fillStyle 定義為 hsl(55 90% 60% / 100%),這是一種黃色,然後呼叫 fillRect() 來建立一個該顏色的矩形。fillRect() 的引數按順序是 x 軸原點、y 軸原點、寬度和高度。fillRect(0, 15, 200, 20) 建立了一個寬度為 200 個單位、高度為 20 個單位的矩形,該矩形距離內容框左側 0 個單位,距離頂部 15 個單位。
我們可以使用 CSS 的 background-size 和 background-position 屬性來重置此背景影像的大小或位置,但這只是我們在 paint worklet 中建立的黃色框的預設大小和位置。
我們嘗試使示例保持簡單。有關更多選項,請檢視 <canvas> 文件。我們稍後也會在本教程中增加一些複雜性。
註冊 Worklet
要使用 paint worklet,我們需要使用 addModule() 註冊它,並在 CSS 中包含它,確保 CSS 選擇器匹配我們 HTML 中的 DOM 節點。
我們的 paint worklet 的設定和設計是在上面顯示的外部指令碼中進行的。我們需要從主指令碼中註冊這個 worklet。
CSS.paintWorklet.addModule("nameOfPaintWorkletFile.js");
這可以透過在主 HTML 的 <script> 或從文件連結的外部 JavaScript 檔案中使用 paint worklet 的 addModule() 方法來完成。
使用 Paint Worklet
在我們的示例中,paint worklet 與主指令碼檔案一起儲存。要使用它,我們首先註冊它。
CSS.paintWorklet.addModule("header-highlight.js");
在 CSS 中引用 Paint Worklet
一旦我們註冊了一個 paint worklet,我們就可以在 CSS 中使用它。像使用任何其他 <image> 型別一樣使用 CSS paint() 函式,使用我們在 paint worklet 的 registerPaint() 函式中使用的相同字串識別符號。
.fancy {
background-image: paint(header-highlight);
}
整合起來
然後,我們可以將 fancy 類新增到頁面上的任何元素,以新增一個黃色框作為背景。
<h1 class="fancy">My Cool Header</h1>
在 支援 CSS Paint API 的瀏覽器中,下面的示例看起來會和上面的圖片一樣。
雖然你無法操作 worklet 的指令碼,但你可以修改 background-size 和 background-position 來改變背景影像的大小和位置。
PaintSize
在上面的示例中,我們建立了一個 20x200 單位的框,距離元素頂部 15 個單位繪製,無論元素大小如何,它都是相同的。如果文字很小,黃色框看起來就像一個巨大的下劃線。如果文字很大,這個框看起來可能像第一個三個字母上方的條形。如果背景影像相對於元素的大小是成比例的,那就更好了——我們可以使用元素的 paintSize 屬性來確保背景影像與元素盒模型大小成比例。
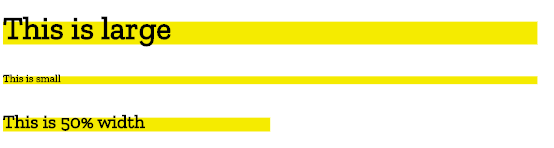
在上圖中,背景與元素的大小成比例。第三個示例在塊級元素上設定了 width: 50%,這使得元素變窄,因此背景影像也變窄。
Paint Worklet
實現此目的的程式碼如下所示:
registerPaint(
"header-highlight",
class {
static get contextOptions() {
return { alpha: true };
}
/*
* ctx is the 2D drawing context
* size is the paintSize, the dimensions (height and width) of the box being painted
*/
paint(ctx, size) {
ctx.fillStyle = "hsl(55 90% 60% / 100%)";
ctx.fillRect(0, size.height / 3, size.width * 0.4, size.height * 0.6);
}
},
);
此程式碼示例與我們的第一個示例有兩處不同:
- 我們包含了一個第二個引數,即 paint size。
- 我們將矩形的尺寸和位置改成了相對於元素盒大小的值,而不是絕對值。
我們可以將第二個引數傳遞給 paint() 函式,以便透過 .width 和 .height 屬性訪問元素的寬度和高度。
我們的標題現在有了一個高亮,該高亮會根據其大小而變化。
使用 Paint Worklet
HTML
<h1 class="fancy">Largest Header</h1>
<h6 class="fancy">Smallest Header</h6>
<h3 class="fancy half">50% width header</h3>
CSS
雖然你無法操作 worklet 的指令碼,但你可以修改元素的 font-size 和 width 來改變背景影像的大小。
.fancy {
background-image: paint(header-highlight);
}
.half {
width: 50%;
}
JavaScript
CSS.paintWorklet.addModule("header-highlight.js");
結果
在 支援 CSS Paint API 的瀏覽器中,下面示例中的元素應該獲得與其字型大小成比例的黃色背景。
自定義屬性
除了訪問元素的大小之外,worklet 還可以訪問 CSS 自定義屬性和常規 CSS 屬性。
registerPaint(
"cssPaintFunctionName",
class {
static get inputProperties() {
return ["PropertyName1", "--customPropertyName2"];
}
static get inputArguments() {
return ["<color>"];
}
static get contextOptions() {
return { alpha: true };
}
paint(drawingContext, elementSize, styleMap) {
// Paint code goes here.
}
},
);
paint() 函式的三個引數包括繪製上下文、paint size 和屬性。為了能夠訪問屬性,我們包含了靜態 inputProperties() 方法,它提供了對 CSS 屬性的即時訪問,包括常規屬性和 自定義屬性,並返回一個屬性名稱的 陣列。我們將在最後一個部分探討 inputArguments。
讓我們建立一個帶有背景影像的列表項,該影像在三種不同的顏色和三種寬度之間旋轉。

為了實現這一點,我們將定義兩個自定義 CSS 屬性:--box-color 和 --width-subtractor。
Paint Worklet
在我們的 worklet 中,我們可以引用這些自定義屬性。
registerPaint(
"boxbg",
class {
static get contextOptions() {
return { alpha: true };
}
/*
* use this function to retrieve any custom properties (or regular properties, such as 'height')
* defined for the element, return them in the specified array
*/
static get inputProperties() {
return ["--box-color", "--width-subtractor"];
}
paint(ctx, size, props) {
/*
* ctx -> drawing context
* size -> paintSize: width and height
* props -> properties: get() method
*/
ctx.fillStyle = props.get("--box-color");
ctx.fillRect(
0,
size.height / 3,
size.width * 0.4 - props.get("--width-subtractor"),
size.height * 0.6,
);
}
},
);
我們在 registerPaint() 類中使用了 inputProperties() 方法來獲取應用於具有 boxbg 類的元素的兩個自定義屬性的值,然後將這些值用於我們的 paint() 函式。inputProperties() 方法可以返回影響元素的全部屬性,而不僅僅是自定義屬性。
使用 Paint Worklet
HTML
<ul>
<li>item 1</li>
<li>item 2</li>
<li>item 3</li>
<li>item 4</li>
<li>item 5</li>
<li>item 6</li>
<li>item 7</li>
<li>item 8</li>
<li>item 9</li>
<li>item 10</li>
<li>item 11</li>
<li>item 12</li>
<li>item 13</li>
<li>item 14</li>
<li>item 15</li>
<li>item 16</li>
<li>item 17</li>
<li>item</li>
</ul>
CSS
在我們的 CSS 中,我們定義了 --box-color 和 --width-subtractor 自定義屬性。
li {
background-image: paint(boxbg);
--box-color: hsl(55 90% 60% / 100%);
}
li:nth-of-type(3n) {
--box-color: hsl(155 90% 60% / 100%);
--width-subtractor: 20;
}
li:nth-of-type(3n + 1) {
--box-color: hsl(255 90% 60% / 100%);
--width-subtractor: 40;
}
JavaScript
在我們的 <script> 中,我們註冊了 worklet。
CSS.paintWorklet.addModule("boxbg.js");
結果
雖然你無法操作 worklet 的指令碼,但你可以在 DevTools 中修改自定義屬性值來改變背景影像的顏色和寬度。
增加複雜性
上面的示例可能看起來不太令人興奮,因為你可以用現有的 CSS 屬性以幾種不同的方式重現它們,例如,透過定位一些裝飾性的 生成內容 和 ::before,或者包含 background: linear-gradient(yellow, yellow) 0 15px / 200px 20px no-repeat; CSS Paint API 之所以如此有趣和強大,是因為你可以建立複雜的影像,傳遞變數,並自動調整大小。
讓我們來看一個更復雜的 paint 示例。
Paint Worklet
registerPaint(
"header-highlight",
class {
static get inputProperties() {
return ["--high-color"];
}
static get contextOptions() {
return { alpha: true };
}
paint(ctx, size, props) {
/* set where to start the highlight & dimensions */
const x = 0;
const y = size.height * 0.3;
const blockWidth = size.width * 0.33;
const highlightHeight = size.height * 0.85;
const color = props.get("--high-color");
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(x, y);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth, y);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth + highlightHeight, highlightHeight);
ctx.lineTo(x, highlightHeight);
ctx.lineTo(x, y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fill();
/* create the dashes */
for (let start = 0; start < 8; start += 2) {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(blockWidth + start * 10 + 10, y);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth + start * 10 + 20, y);
ctx.lineTo(
blockWidth + start * 10 + 20 + highlightHeight,
highlightHeight,
);
ctx.lineTo(
blockWidth + start * 10 + 10 + highlightHeight,
highlightHeight,
);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth + start * 10 + 10, y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fill();
}
} // paint
},
);
使用 Paint Worklet
然後,我們可以建立一個簡單的 HTML 來接受此影像作為背景。
<h1 class="fancy">Largest Header</h1>
<h3 class="fancy">Medium size header</h3>
<h6 class="fancy">Smallest Header</h6>
我們為每個標題提供了不同的 --high-color 自定義屬性值。
.fancy {
background-image: paint(header-highlight);
}
h1 {
--high-color: hsl(155 90% 60% / 70%);
}
h3 {
--high-color: hsl(255 90% 60% / 50%);
}
h6 {
--high-color: hsl(355 90% 60% / 30%);
}
然後我們註冊我們的 worklet。
CSS.paintWorklet.addModule("header-highlight.js");
結果如下所示
雖然你無法編輯 worklet 本身,但你可以嘗試修改 CSS 和 HTML。也許可以嘗試在標題上使用 scale 和 rotate?
你可以嘗試不使用 CSS Paint API 來建立上面的背景影像。這是可行的,但你必須為每個想要的顏色宣告一個不同且相當複雜的線性漸變。使用 CSS Paint API,一個 worklet 可以被重用,例如在這裡傳入不同的顏色。
傳遞引數
注意: 以下示例需要啟用 Chrome 或 Edge 中的實驗性 Web Platform 功能標誌,方法是訪問 about://flags。
使用 CSS Paint API,我們不僅可以訪問自定義屬性和常規屬性,還可以將自定義引數傳遞給 paint() 函式。
我們可以在 CSS 中呼叫函式時新增這些額外的引數。假設我們有時想描邊背景而不是填充它——讓我們為此場合傳遞一個額外的引數。
li {
background-image: paint(hollow-highlights, stroke);
}
現在,我們可以在 registerPaint() 類中使用 inputArguments() 方法來訪問我們新增到 paint() 函式中的自定義引數。
class Worklet {
static get inputArguments() {
return ["*"];
}
// …
}
然後我們就可以訪問該引數了。
class Worklet {
// …
paint(ctx, size, props, args) {
// use our custom arguments
const hasStroke = args[0].toString();
// if stroke arg is 'stroke', don't fill
if (hasStroke === "stroke") {
ctx.fillStyle = "transparent";
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
}
// …
}
// …
}
我們還可以指定我們想要的引數型別。
假設我們新增第二個引數,指定我們想要的描邊畫素寬度。
li {
background-image: paint(hollow-highlights, stroke, 10px);
}
當我們 get 我們的引數列表時,我們可以專門要求一個 <length> 單位。
class Worklet {
// …
static get inputArguments() {
return ["*", "<length>"];
}
// …
}
在這種情況下,我們專門請求了 <length> 屬性。返回陣列的第一個元素將是 CSSUnparsedValue。第二個將是 CSSStyleValue。
如果自定義引數是 CSS 值,例如單位,我們可以透過在 registerPaint() 函式中檢索它時使用值型別關鍵字來呼叫 Typed OM CSSStyleValue 類(及其子類)。
現在我們可以訪問 type 和 value 屬性,這意味著我們可以直接獲得畫素數和數字型別。(誠然,ctx.lineWidth 接受一個浮點數作為值而不是帶有長度單位的值,但僅作示例……)
class Worklet {
// …
paint(ctx, size, props, args) {
const strokeWidth = args[1];
if (strokeWidth.unit === "px") {
ctx.lineWidth = strokeWidth.value;
} else {
ctx.lineWidth = 1.0;
}
// …
}
// …
}
值得注意的是,使用自定義屬性來控制 worklet 的不同部分與此處設定的引數之間的區別。自定義屬性(實際上是樣式圖上的任何屬性)是全域性的——它們也可以在我們的 CSS(和 JS)的其他地方使用。
例如,你可能有一個 --main-color,它對於在 paint() 函式中設定顏色很有用,但也可以用於在 CSS 的其他地方設定顏色。如果你想專門更改它以用於 paint,可能會很困難。這就是自定義引數功能派上用場的地方。另一種思考方式是,引數用於控制你實際繪製的內容,而屬性用於控制樣式。

現在我們可以真正看到這個 API 的優勢了,如果我們能夠透過自定義屬性和額外的 paint() 函式引數從 CSS 控制大量繪製引數,那麼我們就可以真正開始構建可重用且高度可控的樣式函數了。
Paint Worklet
registerPaint(
"hollow-highlights",
class {
static get inputProperties() {
return ["--box-color"];
}
// Input arguments that can be passed to the `paint` function
static get inputArguments() {
return ["*", "<length>"];
}
static get contextOptions() {
return { alpha: true };
}
paint(ctx, size, props, args) {
// ctx -> drawing context
// size -> size of the box being painted
// props -> list of custom properties available to the element
// args -> list of arguments set when calling the paint() function in the CSS
// where to start the highlight & dimensions
const x = 0;
const y = size.height * 0.3;
const blockWidth = size.width * 0.33;
const blockHeight = size.height * 0.85;
// the values passed in the paint() function in the CSS
const color = props.get("--box-color");
const strokeType = args[0].toString();
const strokeWidth = parseInt(args[1], 10);
// set the stroke width
ctx.lineWidth = strokeWidth ?? 1.0;
// set the fill type
if (strokeType === "stroke") {
ctx.fillStyle = "transparent";
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
} else if (strokeType === "filled") {
ctx.fillStyle = color;
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
} else {
ctx.fillStyle = "none";
ctx.strokeStyle = "none";
}
// block
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(x, y);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth, y);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth + blockHeight, blockHeight);
ctx.lineTo(x, blockHeight);
ctx.lineTo(x, y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
// dashes
for (let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
let start = i * 2;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.moveTo(blockWidth + start * 10 + 10, y);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth + start * 10 + 20, y);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth + start * 10 + 20 + blockHeight, blockHeight);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth + start * 10 + 10 + blockHeight, blockHeight);
ctx.lineTo(blockWidth + start * 10 + 10, y);
ctx.closePath();
ctx.fill();
ctx.stroke();
}
} // paint
},
);
使用 Paint Worklet
我們可以設定不同的顏色、描邊寬度,並選擇背景影像是填充還是鏤空。
li {
--box-color: hsl(155 90% 60% / 50%);
background-image: paint(hollow-highlights, stroke, 5px);
}
li:nth-of-type(3n) {
--box-color: hsl(255 90% 60% / 50%);
background-image: paint(hollow-highlights, filled, 3px);
}
li:nth-of-type(3n + 1) {
--box-color: hsl(355 90% 60% / 50%);
background-image: paint(hollow-highlights, stroke, 1px);
}
在我們的 <script> 中,我們註冊了 worklet。
CSS.paintWorklet.addModule("hollow.js");